The first choice matters.
Start with KESIMPTA® (ofatumumab)
.
Annualized Relapse Rate (ARR) With KESIMPTA
Pivotal-trial ARR Data
Superior ARR reductions up to 58% vs Aubagio® (teriflunomide)1
Phase 3 study results: Respectively for each trial, results for the primary end point vs teriflunomide: reduction of ARR: 51% (0.11 vs 0.22), 58% (0.10 vs 0.25); for the key secondary end points vs teriflunomide: reduction of number of Gd+ T1 lesions per scan: 98% (0.01 vs 0.46), 94% (0.03 vs 0.52); reduction of annualized rate of NE T2 lesions: 82% (0.72 vs 4.00), 85% (0.64 vs 4.16); 3-month CDP risk reduction of 34% (10.9 vs 15.0).1
ASCLEPIOS I & II study design: ASCLEPIOS I and II were 2 identical, randomized, active-controlled, double-blind Phase 3 studies in patients with relapsing MS, approximately 40% of whom were DMT treatment naïve. Patients were randomized to double-dummy SC KESIMPTA (20 mg every 4 weeks) or oral Aubagio® (teriflunomide) (14 mg daily) for up to 30 months. Primary end point was ARR. Key secondary end points were number of Gd+ T1 lesions and annualized rate of NE T2 lesions, and reduction in risk of 3-month CDP. Treatment duration was variable based on end-of-study criteria. Maximum duration: 120 weeks; median duration: 85 weeks.1
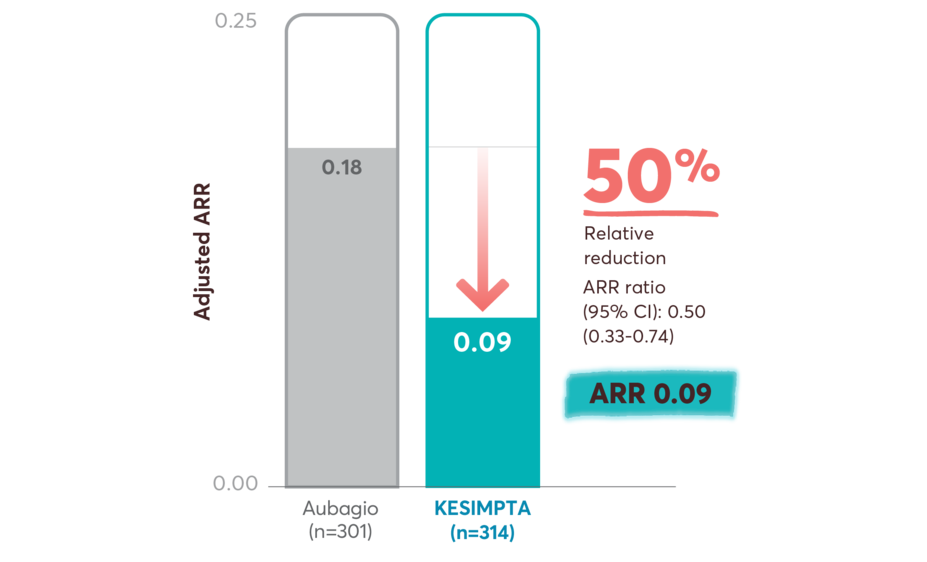
Treatment-naïve ARR Data
ARR reductions in recently diagnosed treatment-naïve patients on first-line KESIMPTA vs Aubagio
Primary end point: relative reduction in annualized relapses vs Aubagio2
This post hoc study assessed the benefit–risk profile of KESIMPTA vs Aubagio, comprising clinical and MRI data in a subpopulation of recently diagnosed treatment-naïve patients from the combined ASCLEPIOS I and II trial populations.2
Post hoc study design: Efficacy and safety data were drawn from the pooled ASCLEPIOS subpopulation of protocol-defined treatment-naïve patients who were within 0.1–2.9 years from diagnosis (median 0.35 and 0.36 years for KESIMPTA and Aubagio patients, respectively). Of the 1882 patients randomly assigned to treatment in ASCLEPIOS I and II, 615 (32.7%) were both recently diagnosed and treatment naïve at baseline (KESIMPTA: 314; Aubagio: 301).2
No conclusions can be drawn.
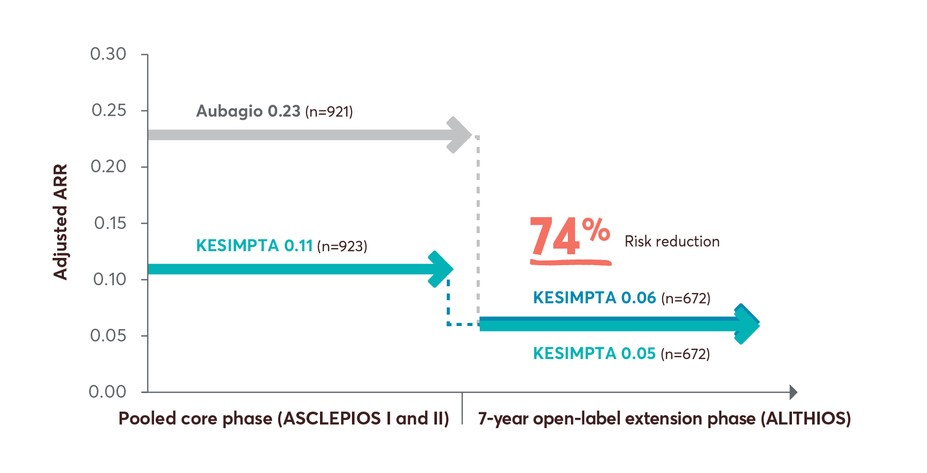
Open-label Extension Study ARR Data
74% risk reduction in ARR up to year 7 in patients who switched from Aubagio to KESIMPTA3
Limitations: This analysis represents chance findings. The open-label extension study is not blinded, not controlled, and includes inherent self-selection bias for remaining in the trial. This study is an ongoing trial and the data presented are an interim analysis. No conclusions of statistical or clinical significance can be drawn.
ALITHIOS study design: ALITHIOS is an open-label, umbrella extension, Phase 3b, single-arm study evaluating long-term (up to 7 years) data. The primary objective was to assess safety and tolerability (N=1969) in patients with RMS who had at least 1 dose of KESIMPTA (20mg SC) (including drop outs) from the ASCLEPIOS I/II, APLIOS, and APOLITOS trials. APLIOS (N=284) was a phase 2,12-week, open-label, parallel-group study. APOLITOS (N=62) is a phase 2, 24-week, double blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group core-part followed by an open-label extension-part for up to 48 weeks, study in Japan and Russia. The secondary objective was to assess efficacy (N=1367) in patients with RMS who had at least 1 dose of KESIMPTA (20mg SC) from the ASCLEPIOS I and II trials who continued or switched to KESIMPTA treatment. A long-term (up to 7 years) analysis (n=465) was conducted to evaluate efficacy in the recently diagnosed treatment-naïve subgroup treated with KESIMPTA.4-9
*Treatment-naïve was defined as patients not on any treatment prior to starting the clinical trials. This includes patients who started on KESIMPTA and patients who switched from Aubagio to KESIMPTA.10
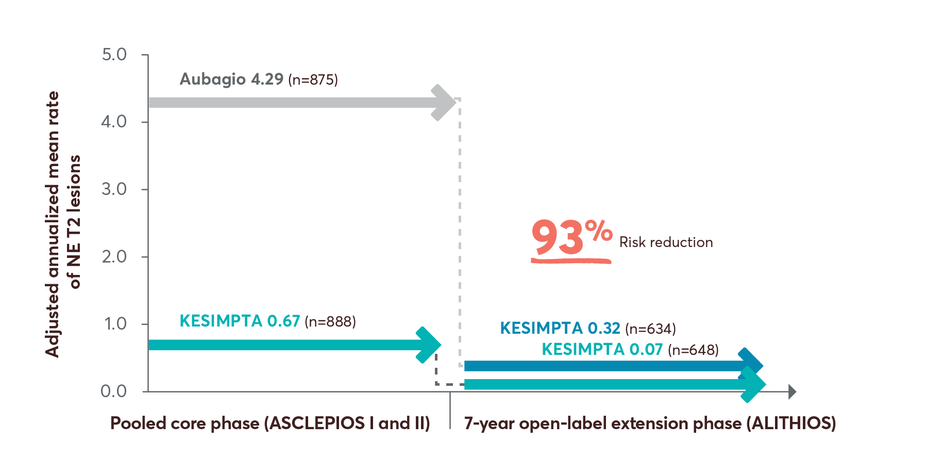
MRI Activity With KESIMPTA
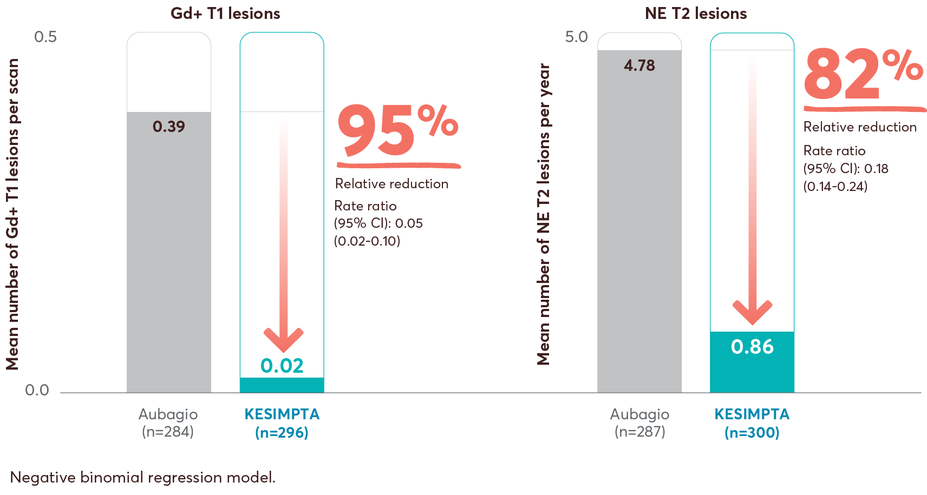
Pivotal-trial MRI Data
Near complete suppression of Gd+ T1 and T2 lesion activity1,11
Treatment-naïve MRI Activity Data
MRI lesion activity in recently diagnosed treatment-naïve patients on first-line KESIMPTA vs Aubagio2
This post hoc study assessed the benefit–risk profile of KESIMPTA vs Aubagio, comprising clinical and MRI data in a subpopulation of recently diagnosed treatment-naïve patients from the combined ASCLEPIOS I and II trial populations.2
Post hoc study design: Efficacy and safety data were drawn from the pooled ASCLEPIOS subpopulation of protocol-defined treatment-naïve patients who were within 0.1–2.9 years from diagnosis (median 0.35 and 0.36 years for KESIMPTA and Aubagio patients, respectively). Of the 1882 patients randomly assigned to treatment in ASCLEPIOS I and II, 615 (32.7%) were both recently diagnosed and treatment naïve at baseline (KESIMPTA: 314; Aubagio: 301).2
No conclusions can be drawn.
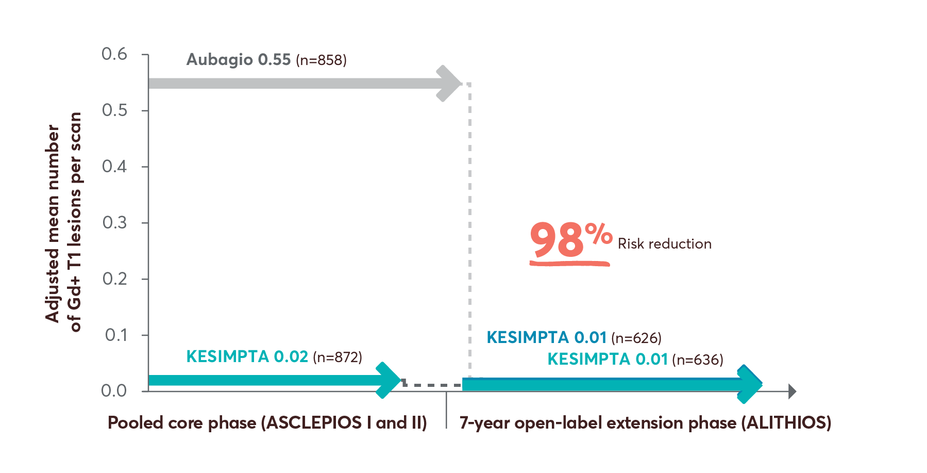
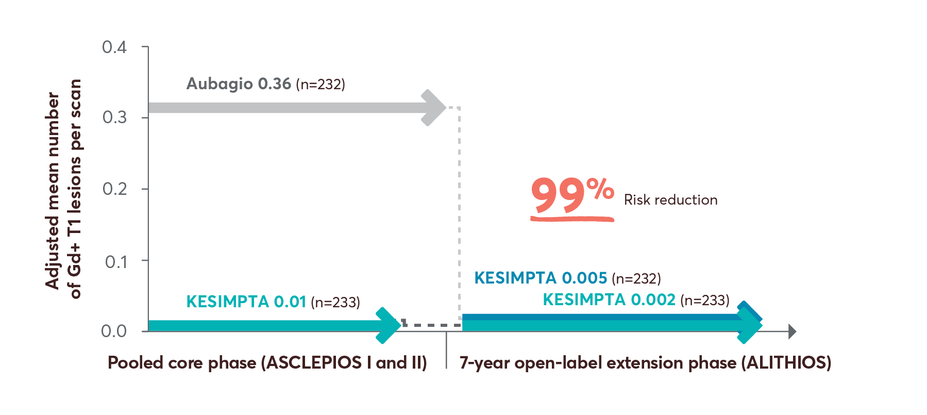
Open-label Extension Study MRI Data
98% risk reduction in Gd+ T1 lesions up to year 7 in patients who switched from Aubagio to KESIMPTA3
T1 Lesions Over Time12
T2 Lesions Over Time13
Limitations: This analysis represents chance findings. The open-label extension study is not blinded, not controlled, and includes inherent self-selection bias for remaining in the trial. This study is an ongoing trial and the data presented are an interim analysis. No conclusions of statistical or clinical significance can be drawn.
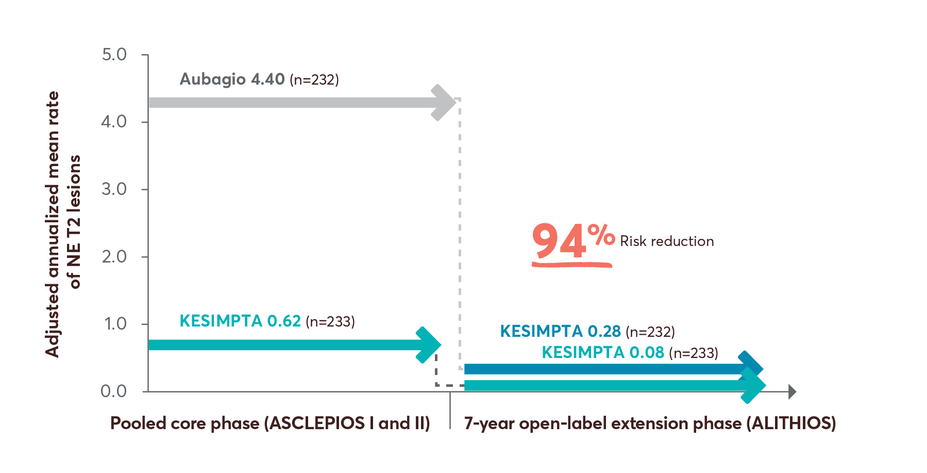
MRI activity with KESIMPTA in treatment-naïve patients up to 7 years4
Gd+ T1 lesions reductions up to 7 years4
NE T2 lesions reductions up to 7 years4
Limitations: This analysis represents chance findings. The open-label extension study is not blinded, not controlled, and includes inherent self-selection bias for remaining in the trial. This study is an ongoing trial and the data presented are an interim analysis. No conclusions of statistical or clinical significance can be drawn.
ALITHIOS study design: ALITHIOS is an open-label, umbrella extension, Phase 3b, single-arm study evaluating long-term (up to 7 years) data. The primary objective was to assess safety and tolerability (N=1969) in patients with RMS who had at least 1 dose of KESIMPTA (20mg SC) (including drop outs) from the ASCLEPIOS I/II, APLIOS, and APOLITOS trials. APLIOS (N=284) was a phase 2,12-week, open-label, parallel-group study. APOLITOS (N=62) is a phase 2, 24-week, double blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group core-part followed by an open-label extension-part for up to 48 weeks, study in Japan and Russia. The secondary objective was to assess efficacy (N=1367) in patients with RMS who had at least 1 dose of KESIMPTA (20mg SC) from the ASCLEPIOS I and II trials who continued or switched to KESIMPTA treatment. A long-term (up to 7 years) analysis (n=465) was conducted to evaluate efficacy in the recently diagnosed treatment-naïve subgroup treated with KESIMPTA.4-9
![“I wanted to start a treatment with powerful efficacy—and dosing that would allow me to continue my full-time coaching career. I love that I can take KESIMPTA whether I’m on the road or relaxing at home.” – CAYLEE R. [25] years old. Volleyball Coach, Outdoor Enthusiast. Started KESIMPTA first line in 2022](https://usim.beprod.kesimptahcp.com/sites/kesimptahcp_com/files/styles/single_featured_content_card_without_content_width_744/public/2025-05/1.0-caylee-quote.jpg?itok=IkGb622e)
CAYLEE R.
25 years old
Volleyball Coach, Outdoor Enthusiast
Started KESIMPTA first line in 2022
"I wanted to start a treatment with powerful efficacy*—and dosing that would allow me to continue my full-time coaching career. I love that I can take KESIMPTA whether I'm on the road or relaxing at home.†"
Real patient taking KESIMPTA who was compensated for time.
Individual results may vary.
No conclusions can be drawn.
The first choice mattered for Caylee. Explore more treatment-naïve patient cases
*As evidenced by reduction in ARR, MRI (Gd+ T1 and T2 lesions), and 3- and 6-month CDP vs teriflunomide. Primary end point: ARR reduction of 51% (0.11 vs 0.22), 58% (0.10 vs 0.25).1,11
†KESIMPTA Sensoready® Pens must be refrigerated at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F). Keep product in the original carton to protect from light until the time of use. Do not freeze. To avoid foaming, do not shake. If necessary, KESIMPTA may be stored at room temperature below 30°C (86°F) for up to 7 days and returned to the refrigerator, to be used within the next 7 days.1
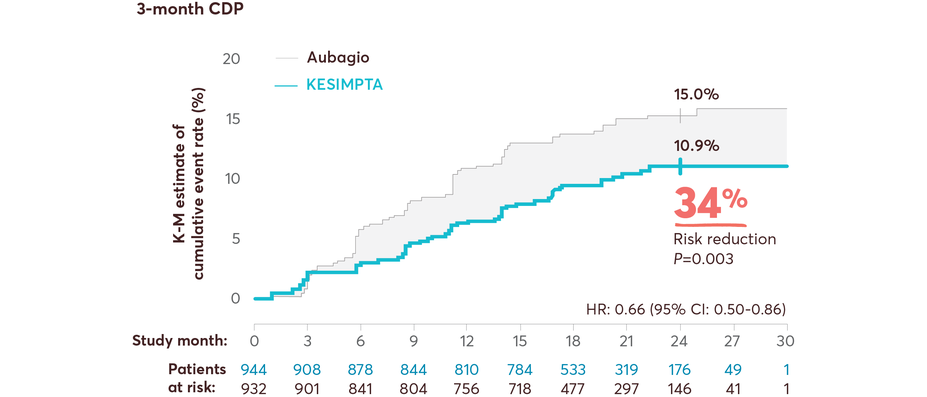
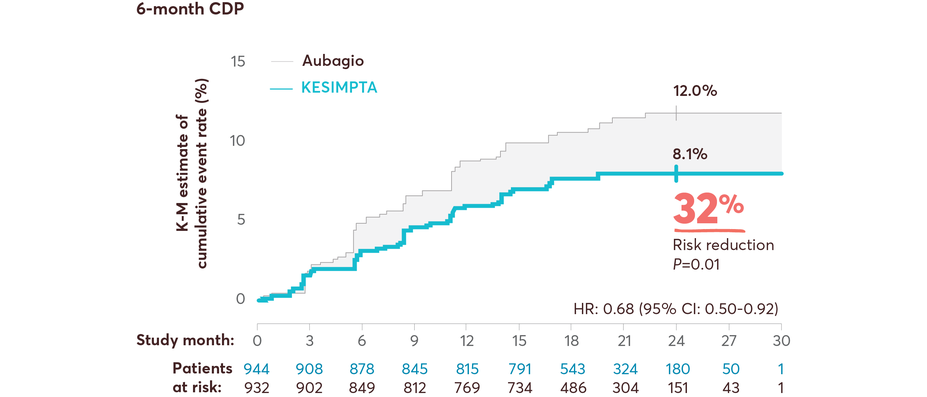
CDP Data
Full Study Population
KESIMPTA showed significant risk reduction in CDP vs Aubagio1,11,14
Results from a prespecified meta-analysis of pooled data from ASCLEPIOS I and II1,11,14
In the extension study, at 7 years
Cumulative 3-month disability progression: KESIMPTA initiators, 26.3%; Aubagio to KESIMPTA switch, 29.8%15
Cumulative 6-month disability progression: KESIMPTA initiators, 22.7%; Aubagio to KESIMPTA switch, 26.2%16
Limitations: This analysis represents chance findings. The open-label extension study is not blinded, not controlled, and includes inherit self-selection bias for remaining in the trial. This study is an ongoing trial and the data presented are an interim analysis. No conclusions of statistical or clinical significance can be drawn.
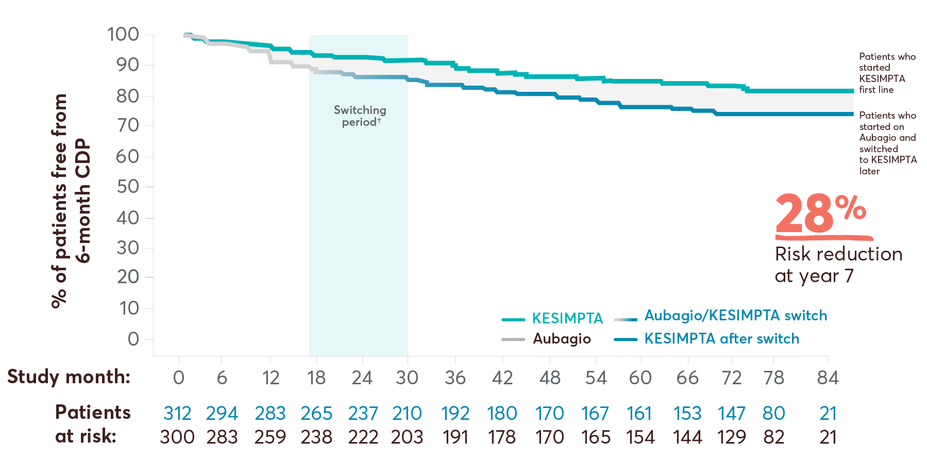
Treatment-naïve CDP Data at Year 7
28% risk reduction in 6-month cumulative disability progression (CDP) at year 7 with KESIMPTA first line vs later switch17
6-month CDP in first-line subgroup vs later switch*
This post hoc study assessed the benefit–risk profile of KESIMPTA vs Aubagio, comprising clinical and MRI data in a subpopulation of recently diagnosed treatment-naïve patients from the combined ASCLEPIOS I and II trial populations.2
Limitations: This analysis represents chance findings. The open-label extension study is not blinded, not controlled, and includes inherent self-selection bias for remaining in the trial. This study is an ongoing trial and the data presented are an interim analysis.2 No conclusions of statistical or clinical significance can be drawn.
Post hoc extension study design: Efficacy and safety data were drawn from the pooled ASCLEPIOS subpopulation of protocol-defined treatment-naïve patients who were within 0.1–2.9 years from diagnosis (median 0.35 and 0.36 years for KESIMPTA and Aubagio patients, respectively). Of the 1882 patients randomly assigned to treatment in ASCLEPIOS I and II, 615 (32.7%) were both recently diagnosed and treatment naïve at baseline (KESIMPTA, 314; Aubagio, 301). 465 recently diagnosed and treatment-naïve patients entered the ALITHIOS trial, and 366/465 (78.7%) of treatment-naïve patients were still receiving KESIMPTA at the 7-year data cutoff (September 25, 2024).2,17 No conclusions can be drawn.
ALITHIOS study design: ALITHIOS is an open-label, umbrella extension, Phase 3b, single-arm study evaluating long-term (up to 7 years) data. The primary objective was to assess safety and tolerability (N=1969) in patients with RMS who had at least 1 dose of KESIMPTA (20mg SC) (including drop outs) from the ASCLEPIOS I/II, APLIOS, and APOLITOS trials. APLIOS (N=284) was a phase 2,12-week, open-label, parallel-group study. APOLITOS (N=62) is a phase 2, 24-week, double blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group core-part followed by an open-label extension-part for up to 48 weeks, study in Japan and Russia. The secondary objective was to assess efficacy (N=1367) in patients with RMS who had at least 1 dose of KESIMPTA (20mg SC) from the ASCLEPIOS I and II trials who continued or switched to KESIMPTA treatment. A long-term (up to 7 years) analysis (n=465) was conducted to evaluate efficacy in the recently diagnosed treatment-naïve subgroup treated with KESIMPTA.4-9
†Switching period refers to the patients started with Aubagio and not applicable to the patients treated with KESIMPTA in the core period; for Aubagio/KESIMPTA group, data from first dose of Aubagio until last dose of KESIMPTA plus 100 days or analysis cutoff date has been used.4
NEDA-3 Data
NEDA-3 Full Study Population
No evidence of disease activity (NEDA-3) for 95% of patients at year 76,18
Treatment-naïve Data
No evidence of disease activity (NEDA-3) for ~96% of treatment-naïve patients at year 74,18
Re-baselining for year 2 (months 12-24) was conducted at month 12 to adjust for impact of disease activity prior to treatment initiation (T2 lesions) and continuing through the first year of treatment. This re-baselining allows for the accurate measure of the disease activity as measured in year 2.19,20
NEDA-3 post hoc analysis limitations: This analysis considers patients without evidence of disease activity (which may also include patients with partially missing information) as NEDA-3. A sensitivity analysis was conducted for the population of patients who completed the full 24 months of treatment.19 No conclusions of clinical outcomes can be drawn.
NEDA-3 post hoc analysis design: All patients from the pivotal trials, full analysis set population (all randomized patients with assigned treatments) who also received KESIMPTA in the ALITHIOS extension study (data cutoff: September 25, 2024) were included in the intent-to-treat principle except for patients who had reached NEDA-3 but discontinued from the study drug prematurely for reasons other than “lack of efficacy” or “death.” The outcomes presented here are the proportion of study patients within a treatment group who met the NEDA-3 criteria vs those who did not. The proportion of patients meeting NEDA-3 criteria was analyzed cross sectionally in 1-year time intervals across 7 years. Within the prespecified time period, patients who achieved NEDA-3 experienced no 6-month CDP; no confirmed relapse; no Gd+ T1 lesions; no NE T2 lesions; and no discontinuation from the study drug due to either lack of efficacy or death.4,19

KARINA L.
Photographer, Mom
"KESIMPTA is my first treatment and my first choice. As a business owner and busy mom, I need to be confident that my treatment will show long-term results."
Real patient taking KESIMPTA who was compensated for time.
Individual results may vary.
See the safety profile of KESIMPTA